Treatment for gum disease can take different approaches, either nonsurgical or surgical, depending on the disease’s stage and your oral and overall health condition. Nonsurgical treatments comprise scaling and root planing, as well as the use of antibiotics. Surgical options involve procedures such as pocket reduction surgery and guided tissue regeneration. Typically, a periodontist, a specialist in gum health, carries out these interventions.
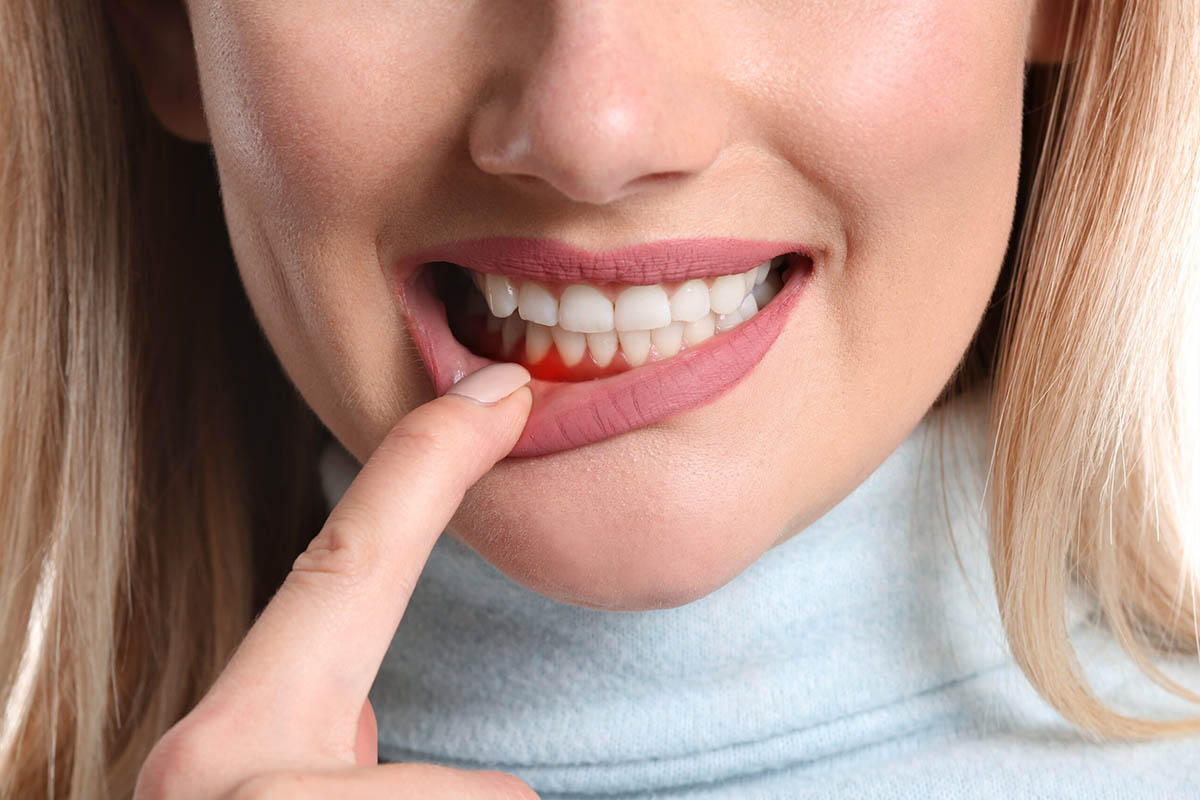

What does gum disease treatment involve?
Gum disease treatment encompasses a variety of dental procedures aimed at reducing infection in the mouth and repairing tissues damaged by periodontal (gum) disease. Typically, these procedures are performed by periodontists, who specialize in gum health. However, general dentists may also treat milder forms of gum disease.
Gum disease develops when plaque and tartar accumulate on the surfaces of your teeth. The bacteria in these substances cause your gums to become red, swollen, and tender. Additionally, your gums may bleed when you brush or floss.
Treating gum disease as early as possible greatly improves your chances of maintaining long-term oral health. In its initial stage, known as gingivitis, gum disease can be reversed. However, if it progresses to periodontitis, the later stages, it can cause damage to your gums and the underlying bone. This leads to the formation of gaps, or periodontal pockets, around your teeth, which further promote infection, tooth looseness, and even tooth loss.
Nonsurgical treatment options for gum disease
Individuals with early-stage gum disease, such as gingivitis or mild periodontitis, can benefit from nonsurgical therapies. The following are nonsurgical treatments commonly used for gum disease:
Dental prophylaxis:
Dental prophylaxis refers to a routine dental cleaning, similar to the regular cleanings many people receive from their hygienist twice a year. During this procedure, a healthcare provider removes plaque and tartar from the surfaces of your teeth.
For individuals with gingivitis (the initial stage of gum disease), professional dental cleanings and improved oral hygiene at home can often reverse the condition. Depending on your specific circumstances, your dentist or hygienist may recommend more frequent cleanings to keep harmful bacteria under control.
Scaling and root planing:
Scaling and root planing, also known as a deep dental cleaning, targets the removal of plaque and tartar deep beneath the gum line, specifically on the surfaces of your tooth roots. Along with thorough cleaning, your periodontist or dental hygienist will smoothen any rough areas on the roots of your teeth. This helps prevent bacteria and plaque from reattaching. Local anesthesia is administered by your periodontist to numb your gums and ensure your comfort during the procedure.
Antibiotic therapy:
Your periodontist may employ antibiotics as a standalone treatment or in combination with other procedures. Commonly used antibiotics for gum disease treatment include minocycline HCl (Arestin®) or chlorhexidine (PerioChip®). These medications can be placed by your periodontist into the periodontal pocket—the space between your gums and teeth.
Laser periodontal therapy:
During this procedure, a small laser is used by your periodontist to remove diseased tissue and eliminate bacteria beneath your gums. In some cases, laser therapy may be recommended as an alternative to traditional gum surgery. Unlike traditional surgery, laser therapy does not require incisions or sutures.
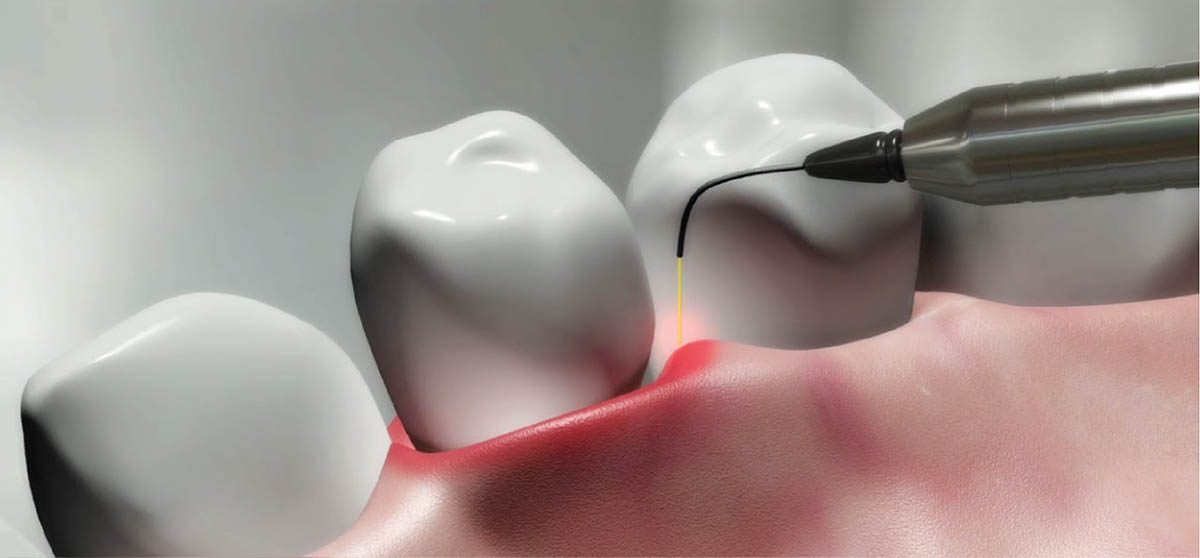
Surgical treatment options for gum disease
Individuals with moderate to advanced periodontal disease typically require surgical interventions. The following are surgical treatments commonly used for gum disease:
Pocket reduction surgery (flap surgery):
In this procedure, your periodontist will create incisions along the gum line, temporarily moving the gums away from your teeth to access the roots. They will then remove tartar buildup and clean the root surfaces. In some cases, they may also reshape damaged bone to eliminate hiding places for bacteria. Finally, the gums are repositioned and sutured back into place.
Bone grafting:
Dental bone grafts involve using your own bone, donated bone, or synthetic bone to rebuild areas that have been damaged by gum disease. The graft acts as a scaffold, holding the space until new bone can regenerate. Periodontists often perform bone grafting in conjunction with pocket reduction surgery.
Gum grafting:
Gum grafting is performed to treat gum recession, a common symptom of periodontal disease where the gums pull away from the teeth. During the surgery, your periodontist uses your own tissue, donated tissue, or synthetic tissue to graft onto areas where the gums have receded. If your own tissue is used, it is typically taken from the roof of your mouth.
Read more: Sinus lift and bone grafting surgery in Turkey
Guided tissue regeneration:
Periodontal disease can create gaps between the tooth root and bone. In guided tissue regeneration, a membrane is placed by your periodontist in the damaged area to prevent gum tissue from growing where bone should be. This allows the body to regenerate bone around the tooth. In many cases, a bone graft is placed during the same procedure to aid in this process.
What is the success rate of gum disease treatment?
Gum disease treatment has shown impressive success rates, with some instances reaching up to 95%. However, the success rates can vary depending on several factors, including the specific procedure performed and the individual’s adherence to proper oral care following treatment.
Treatment for gum disease can significantly improve the long-term prognosis of teeth affected by periodontitis. In many cases, such therapy can save teeth that would have otherwise been deemed hopeless without intervention.
It is essential to recognize that gum disease cannot be completely cured; it can only be managed. The focus of treatments is on prevention and management rather than a complete cure.
Recovery time for gum disease
The recovery time for gum disease treatment varies depending on the specific type of treatment you undergo. If you receive scaling and root planing, you typically won’t require any downtime and can resume your regular activities immediately. However, for more advanced procedures targeting severe periodontal disease, such as flap surgery, bone grafts, or gum grafts, the recovery period usually ranges from one to four weeks.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of laser treatment for gum disease?
Advantages of laser treatment for gum disease:
There are several notable benefits associated with laser therapy:
- Accuracy and precision: Periodontal lasers are able to target and remove diseased tissue while preserving healthy tissue, ensuring a more precise treatment.
- Reduced pain: Laser therapy is generally less invasive compared to traditional gum surgery, resulting in reduced pain, swelling, and discomfort for patients who undergo this procedure.
- Shorter recovery time: The recovery period after laser therapy tends to be shorter compared to traditional gum surgery. However, the exact healing time can vary depending on the extent of treatment needed and the severity of the disease.
Disadvantages of laser treatment for gum disease:
There is one major drawback associated with periodontal laser therapy:
- Limited effectiveness for advanced periodontal disease: Laser treatment may not always be as effective when dealing with advanced periodontal disease. In cases of severe periodontitis, a periodontist may recommend traditional flap surgery as a more suitable treatment option.
It is important to consult with your periodontist to determine the most appropriate treatment approach for your specific condition.
Gum disease treatment at IstanBest Clinic encompasses a variety of surgical and nonsurgical procedures aimed at addressing gingivitis and periodontitis. Our professional treatment is crucial for effectively treating and managing these conditions. It’s important to note that gum disease cannot be cured, but it can be managed through proper treatment and improved oral hygiene practices at home. At IstanBest Clinic, we are committed to providing comprehensive care to help you effectively manage gum disease and maintain optimal oral health.